java configuration方式
- 上面是以xml文件的方式配置,接下来介绍以自定义java类的方式来配置spring security
可先在719行:自定义过滤器一节了解认证流程。
1. 注册DelegatingFilterProxy
package com.study.config; import org.springframework.security.web.context.*; public class SecurityWebApplicationInitializer extends AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer { @Override protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() { return new Class[] { WebSecurityConfig.class }; } }继承该类相当于在web.xml中:
<filter> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class> </filter>重写getRootConfigClasses()相当于把下一步Spring Security的配置加载到程序中。
2. Spring Security安全配置
package com.study.config; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.security.authentication.encoding.Md5PasswordEncoder; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.WebSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterSecurityInterceptor; import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.AntPathRequestMatcher; import com.study.security.MyFilterSecurityInterceptor; @Configuration @EnableWebSecurity //启用web安全功能 public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { // @Resource // private DataSource dataSource; //配置自定义的用户服务(即选择用户信息的查询方式是从用户库或数据库,怎么查询) @Resource(name="myUserDetailService") private UserDetailsService myUserDetailService; //第3点:自定义用户验证 @Resource private AuthenticationProvider myAuthenticationProvider; //自定义认证成功处理器 @Resource private AuthenticationSuccessHandler myAuthenticationSuccessHandler; //第4点:自定义拦截器(自定义权限验证,而不是拦截规则) @Resource private MyFilterSecurityInterceptor myFilterSecurityInterceptor; /** * 密码加密 */ @Bean public BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){ return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); } /** * 自定义认证过程 */ @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { /* 不重写的话默认为 auth .inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("user").password("password").roles("USER"); //默认准备了一个用户 */ //方式一:内存用户存储 /* auth.inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("user1").password("123456").roles("USER").and() .withUser("admin").password("admin").roles("USER","ADMIN"); */ // //方式二:数据库表认证 /* auth.jdbcAuthentication().dataSource(dataSource) .usersByUsernameQuery("select username,password,enable from t_user where username=?") .authoritiesByUsernameQuery("select username,rolename from t_role where username=?"); */ //方式三:自定义数据库 auth.userDetailsService(myUserDetailService) .passwordEncoder(new Md5PasswordEncoder()); //加后MyAuthenticationProvider里比对密码时能把表单的明文和数据库的密文对应 //自定义用户验证 auth.authenticationProvider(myAuthenticationProvider); } // 暴露默认的authenticationManager // @Override // public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception { // return super.authenticationManagerBean(); // } /** * 配置Spring Security的Filter链 */ @Override public void configure(WebSecurity web)throws Exception { // 设置不拦截规则 web.ignoring().antMatchers("/css/**","/js/**","/img/**","/font-awesome/**"); } /** * 配置如何通过拦截器保护请求:配置了自定义的过滤器、自定义登录登出页面 * 前端请求的时候先经过这里检测请求是否需要验证或权限,不需要的话直接把请求分发给controller去处理,需要就认证过了再分发 */ @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .addFilterBefore(myFilterSecurityInterceptor, FilterSecurityInterceptor.class)//在正确的位置添加我们自定义的过滤器 .authorizeRequests() //需要权限,权限符合与否由上面过滤器检查 .antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") //以admin开头的url需要admin权限 .antMatchers("/db/**").access("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')") .anyRequest().authenticated() //不与以上匹配的所有请求只需要登录验证 // .and().formLogin().and() //and相当于节点结束 // .httpBasic(); // 自定义登录页面:permitAll,允许all用户访问login页面 //未登录前访问受保护资源被转回login .and() /*直接/jsp/login的话会分配给controller去处理,则需要写controller映射到登录页;请求login.jsp报404 有后缀则直接请求资源,那么url=/login还是由controller处理; 那么最好是加后缀,才不用再走controller*/ .formLogin().loginPage("/jsp/login.jsp") .failureUrl("/jsp/login.jsp?error=1") //表单提交地址,4.x默认为/login;无需认证,但是请求方式必须post .loginProcessingUrl("/spring_security_check") .usernameParameter("username") .passwordParameter("password") .successHandler(myAuthenticationSuccessHandler) //自定义认证成功处理器 //.failureHandler(myAuthenticationFailureHandler) .permitAll() //这里也是,要么配资源路径,要么配有controller处理的url .defaultSuccessUrl("/index.do") .and() //配置session管理 .sessionManagement() /*指定了maximumSessions需配合web.xml中HttpSessionEventPublisher 清理掉过期session*/ .maximumSessions(1) .expiredUrl("/login.jsp?expired=1"); //如果(默认)开启了CSRF,退出则需要使用POST访问,可使用以下方式解决,但不推荐 http.logout().logoutRequestMatcher(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout")) //登陆成功后跳转的地址,以及删除的cookie名称 .logoutSuccessUrl("/jsp/login.jsp?error=logout") .invalidateHttpSession(true); } }- 接收到请求,先在spring security中是否有符合的(/login、/logout、/spring_security_check、/**/favicon.ico、…),出现Checking match of request : ‘/login’; against ‘/logout’或Request ‘GET /login’ doesn’t match ‘POST /spring_security_check都表示当前请求与已存在url不匹配,后者指明spring_security_check必须是post形式的,若不匹配,则检测用户是否已认证,未认证,后台报AccessDenyException,前端转回login页面,已认证,分发给controller处理。所以用户请求的资源是他不能访问的就会报AccessDenyException。
- 未登录时用户为匿名用户

- 登录后若未给用户设置权限,则用户为无权限

- 所以给请求设置权限,如果没有指定权限,则至少不能是匿名用户
大致相当于配置
<!-- 获取访问url对应的所有权限 --> <beans:bean id="secureResourceFilterInvocationDefinitionSource" class="com.ultrapower.me.util.security.interceptor.SecureResourceFilterInvocationDefinitionSource" /> <!-- 校验用户的权限是否足够 --> <beans:bean id="mesecurityAccessDecisionManager" class="com.ultrapower.me.util.security.interceptor.SecurityAccessDecisionManager" /> <!-- 自定义权限认证 --> <beans:bean id="securityInterceptor" class="com.ultrapower.me.util.security.interceptor.SecurityInterceptor"> <beans:property name="authenticationManager" ref="authenticationManager"/> <beans:property name="accessDecisionManager" ref="mesecurityAccessDecisionManager"/> <beans:property name="securityMetadataSource" ref="secureResourceFilterInvocationDefinitionSource" /> </beans:bean> <!-- 用户服务 --> <beans:bean id="myUserDetailsService" class="com.ultrapower.me.util.security.support.myUserDetailsService"></beans:bean> <!-- 自定义用户验证--> <beans:bean id="myAuthenticationProvider" class="com.security.MyAuthenticationProvider"> <beans:property name="userDetailsService" ref="myUserDetailsService" /> </beans:bean> <!-- 1、自定义权限认证:依赖上面的bean --> <http auto-config="true" use-expressions="false"> <intercept-url pattern="/login.jsp*" access="IS_AUTHENTICATED_ANONYMOUSLY"/> <intercept-url pattern="/**" access="ROLE_USER"/> <form-login login-page="/login.jsp" default-target-url="/jsp/index/main.jsp" authentication-failure-url="/login.jsp?error=true"/> <custom-filter before="FILTER_SECURITY_INTERCEPTOR" ref="securityInterceptor"/> </http> <!-- 2、自定义用户验证:依赖上面的bean--> <authentication-manager alias="authenticationManager"> //起别名,方便被下面自定义拦截器依赖 <!--自定义用户验证--> <authentication-provider ref="myAuthenticationProvider" /> <!--只自定义用户服务而不需要自定义用户验证的话 <authentication-provider user-service-ref="myUserDetailsService">--> <password-encoder ref="myPasswordEncoder"/> </authentication-provider> </authentication-manager>
一些自定义方式
简单的自定义登录页面对比
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .authorizeRequests() .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() .formLogin() .and() .httpBasic(); }相当于
<http> <intercept-url pattern="/**" access="authenticated"/> <form-login /> <http-basic /> </http>自定义权限
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .authorizeRequests() //需要权限 .antMatchers("/resources/**", "/signup", "/about").permitAll() .antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") //使用hasRole()可以不写ROLE_前缀,但实际上我们指定的权限还是ROLE_ADMIN .antMatchers("/db/**").access("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')") /*按照顺序匹配,下面是对的*/ //.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") //.antMatchers("/**").hasRole("USER") /*下面是错的,因为满足第一个规则后将不会检查第二条,所以要从精确到广泛配置*/ //.antMatchers("/**").hasRole("USER") //.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") .anyRequest().authenticated() //需要验证 .and() // ... .formLogin(); }自定义登出页面
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .logout() .logoutUrl("/my/logout") .logoutSuccessUrl("/my/index") .logoutSuccessHandler(logoutSuccessHandler) //自定义登出成功后的操作,上一行失效 .invalidateHttpSession(true) //添加一个自定义登出处理器,SecurityContextLogoutHandler默认是最后一个处理器 .addLogoutHandler(logoutHandler) .deleteCookies(cookieNamesToClear) .and() ... }一般前面两步都是直接用配置文件实现,然后注入自定义UserDetailServiceImpl,也就这个要用java写而已
自定义用户服务
- 如果是要用数据库的话那肯定是要的,首先是用户实体类UserDetails必须改为符合数据库的字段,默认的也就用户名、密码加权限列表了,其次获取用户信息UserDetialsService的方式也要改成从数据库获取.
首先是UserDetailsService,主要是根据用户名从数据库找出用户all信息,主要是用户名、密码和权限列表
package com.study.security; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.List; import java.util.Set; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority; import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import com.study.model.Resources; import com.study.model.User; import com.study.service.ResourcesService; import com.study.service.UserService; @Component("myUserDetailService") public class MyUserDetailServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService{ //这里可以来个日志 @Resource private UserService userService; @Resource private ResourcesService resourcesService; @Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException { //通过用户名查询用户信息 User user = userService.findUserByName(username); //系统实体类User implement UsersService,系统service类userService if(user ==null) throw new UsernameNotFoundException(username+" not exist!"); //存放角色名的集合 Set<GrantedAuthority> authSet = new HashSet<GrantedAuthority>(); //系统实体类Resources,即各个url Resources resources = new Resources(); resources.setUsername(username); //找到特定用户名能访问的url集合 List<Resources> list = resourcesService.loadMenu(resources); for (Resources r : list) { //根据资源找到角色名,添加到角色名集合 authSet.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_" +r.getResKey())); //resKey:资源名,拼成角色名 } /* username():登录用户名 password():从数据库查出来的密码 enable: 用户状态,true为有效,false无效 accoutNonExpired,credentialsNonExpired,accountNonLocked roles: Collections集合,当前登录用户的角色列表 */ return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(), user.getEnable()==1?true:false, true, true, true, authSet); //返回的user不为空,则验证通过 } }系统实体类User实现UserDetails,主要是查询数据库所有权限,返回权限列表
public class User implements UserDetails { private static final long serialVersionUID = 8026813053768023527L; private String name; private String password; private Set<Role> roles; //可以不写 //其他属性,随便,自定义 /** * 返回系统所有角色 */ @Override public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() { //根据自定义逻辑来返回用户权限,如果用户权限返回空或者和拦截路径对应权限不同,验证不通过 if(!roles.isEmpty()){ List<GrantedAuthority> list = new ArrayList<GrantedAuthority>(); GrantedAuthority au = new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role.getrName()); list.add(au); return list; } return null; } /** * 默认有一个方法返回当前用户的角色列表,后面介绍了它的重写;可选的 */ @Override public String getPassword() { return this.password; } @Override public String getUsername() { return this.username; } /* *帐号是否不过期,false则验证不通过 */ @Override public boolean isAccountNonExpired() { return true; } /* * 帐号是否不锁定,false则验证不通过 */ @Override public boolean isAccountNonLocked() { return true; } /* * 凭证是否不过期,false则验证不通过 */ @Override public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() { return true; } /* * 该帐号是否启用,false则验证不通过 */ @Override public boolean isEnabled() { return true; } }- User类代码实例:llcweb/domain/models/
- 数据库表介绍:五张表————用户表、角色表、资源表、用户角色表、角色资源表。给用户分配角色,给角色分配资源(即权限)。一个用户可以对应多个角色,一个角色可以对应多个资源。
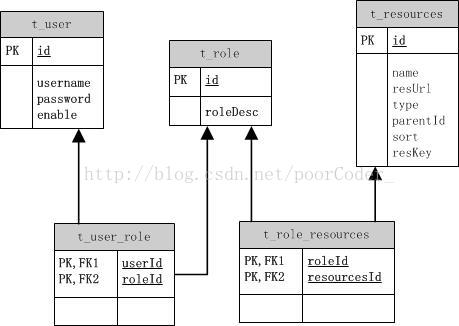
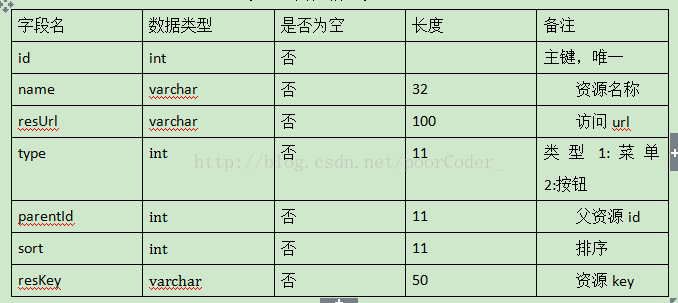
- 其中资源表t_resources包含了后台系统的所有url
- resKey即角色名
自定义过滤器
- 首先整理spring security的步骤:
- 在spring security中每一个url都是一个资源,系统启动时,spring security第一个拦截器FilterSecurityInterceptor调用SecurityMetadataSource将所有url与其权限对应。
- 当用户发起请求时,spring security检查该请求是否需要特定权限(需不需要都在WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter中指定了),不需要的话直接访问,连是否登录都不验证。
- 需要权限,AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter先验证当前用户是否已登录,否则跳转登录页面。
- 已登录,FilterSecurityInterceptor判断该用户是否拥有当前请求所需的权限,有则允许访问,没有则给出提示信息。
- 我们这一节说的过滤器特指这个FilterSecurityInterceptor。基于数据库的权限验证必须要自定义过滤器,因为它主要就是做权限验证的,包括资源与权限对应关系的查询、当前用户是否持有请求资源所需权限的判断。
前面不是用java注册spring security的话就需要以下配置
<!--还要在http中添加<custom-filter before="FILTER_SECURITY_INTERCEPTOR" ref="securityInterceptor"/>--> <!--ProviderManager类的实例注入authenticationManager--> <authentication-manager alias="authenticationManager"> <!-- 获取访问url对应的所有权限 --> <beans:bean id="secureResourceFilterInvocationDefinitionSource" class="com.ultrapower.me.util.security.interceptor.SecureResourceFilterInvocationDefinitionSource" /> <!-- 校验用户的权限是否足够 --> <beans:bean id="mesecurityAccessDecisionManager" class="com.ultrapower.me.util.security.interceptor.SecurityAccessDecisionManager" /> <!-- 自定义拦截器:依赖上面的bean --> <beans:bean id="securityInterceptor" class="com.ultrapower.me.util.security.interceptor.SecurityInterceptor"> <beans:property name="authenticationManager" ref="authenticationManager"/> <beans:property name="accessDecisionManager" ref="mesecurityAccessDecisionManager"/> <beans:property name="securityMetadataSource" ref="secureResourceFilterInvocationDefinitionSource" /> </beans:bean>开始自定义过滤器
package com.study.security; import java.io.IOException; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; import javax.annotation.Resource; import javax.servlet.Filter; import javax.servlet.FilterChain; import javax.servlet.FilterConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.ServletRequest; import javax.servlet.ServletResponse; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.security.access.SecurityMetadataSource; import org.springframework.security.access.intercept.AbstractSecurityInterceptor; import org.springframework.security.access.intercept.InterceptorStatusToken; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.configuration.AuthenticationConfiguration; import org.springframework.security.web.FilterInvocation; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class MyFilterSecurityInterceptor extends AbstractSecurityInterceptor implements Filter { //所有资源与权限的关系(需要在外面自定义):获取请求资源的权限 @Autowired private MySecurityMetadataSource securityMetadataSource; //用户是否拥有所请求资源的权限(需要在外面自定义):判断是否拥有请求资源所需的权限 @Autowired private MyAccessDecisionManager accessDecisionManager; /* 默认装配够用了 @Resource(name="myAuthenticationManager") private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager; */ @Resource private AuthenticationConfiguration authenticationConfiguration; // @Autowired // public void setAuthenticationConfiguration(AuthenticationConfiguration authenticationConfiguration) { // this.authenticationConfiguration = authenticationConfiguration; // } @PostConstruct public void init() throws Exception{ super.setAccessDecisionManager(accessDecisionManager); super.setAuthenticationManager(authenticationConfiguration.getAuthenticationManager()); } @Override public SecurityMetadataSource obtainSecurityMetadataSource() { return this.securityMetadataSource; } @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { FilterInvocation fi = new FilterInvocation(request, response, chain); /*beforeInvocation做的事*/ //super.beforeInvocation(fi);源码 //获取请求资源的权限 //执行Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = SecurityMetadataSource.getAttributes(object); //object为FilterInvocation对象 //是否拥有权限;authentication:封装了用户拥有的权限 //this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes); InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi); try { //执行下一个拦截器 fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse()); } finally { super.afterInvocation(token, null); } } @Override public void init(FilterConfig arg0) throws ServletException { } @Override public void destroy() { } @Override public Class<? extends Object> getSecureObjectClass() { //下面的MyAccessDecisionManager的supports方法必须返回true,否则会提醒类型错误 return FilterInvocation.class; } }自定义过滤器需要用到的用户是否拥有所请求资源的权限:MyAccessDecisionManager。默认使用AbstractAccessDecisionManager,具体是继承了AbstractAccessDecisionManager的AffirmativeBased,还有其他其他的决策管理器,不过不知道怎么启用,只是投票方式不同而已,有的是只要有赞成票就通过权限验证,有的是只要有反对票就不通过。但是看不懂底层是根据什么投赞成票和反对票的,反正不通过就抛AccessDenyException,一层层向上抛出,由ExceptionTranslationFilter打印异常日志。
package com.study.security; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Iterator; import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDecisionManager; import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException; import org.springframework.security.access.ConfigAttribute; import org.springframework.security.authentication.InsufficientAuthenticationException; import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication; import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class MyAccessDecisionManager implements AccessDecisionManager { /** * 决定authentication拥有的权限中有没有指定资源的权限 * object:受保护对象,其可以是一个MethodInvocation、JoinPoint或FilterInvocation * authentication:封装了用户拥有的权限 * configAttributes:受保护对象的相关配置属性,主要是访问资源需要的权限 */ public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException, InsufficientAuthenticationException { if(configAttributes == null) { return; } //所请求的资源需要的权限(一个资源对多个权限) Iterator<ConfigAttribute> iterator = configAttributes.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()) { ConfigAttribute configAttribute = iterator.next(); //访问所请求资源所需要的权限 String Permission = configAttribute.getAttribute(); System.out.println("needPermission is " + Permission); //用户所拥有的权限authentication for(GrantedAuthority ga : authentication.getAuthorities()) { if(Permission.equals(ga.getAuthority())) { return; } } } //没有权限,后台抛异常而前端显示access-denied-page页面 throw new AccessDeniedException(" 没有权限访问或未重新登录! "); } /** * 判断AccessDecisionManager是否能够处理对应的ConfigAttribute */ public boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return true; } /** * 判断AccessDecisionManager是否支持对应的受保护对象类型 */ public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return true; } }自定义过滤器需要用到的获取资源权限(即查询t_resources表中所有resKey与resUrl的关系):MySecurityMetadataSource
package com.study.security; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.security.access.ConfigAttribute; import org.springframework.security.access.SecurityConfig; import org.springframework.security.web.FilterInvocation; import org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import com.study.dao.ResourcesDao; import com.study.model.Resources; @Component public class MySecurityMetadataSource implements FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource { @Resource private ResourcesDao resourcesDao; private static Map<String, Collection<ConfigAttribute>> resourceMap = null; public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAllConfigAttributes() { return null; } public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) { return true; } /** * @PostConstruct是Java EE 5引入的注解, * Spring允许开发者在受管Bean中使用它。当DI容器实例化当前受管Bean时, * @PostConstruct注解的方法会被自动触发,从而完成一些初始化工作 */ @PostConstruct private void loadResourceDefine() { //加载所有资源与权限的关系 if (resourceMap == null) { resourceMap = new HashMap<String, Collection<ConfigAttribute>>(); //数据库查询所有资源 List<Resources> list = resourcesDao.queryAll(new Resources()); //Resources:本项目自定义的实体 for (Resources resources : list) { Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes = new ArrayList<ConfigAttribute>(); // 通过资源名称来表示具体的权限 注意:必须"ROLE_"开头 /*SecurityConfig:ConfigAttribute实现类; 只有一个成员,是个常量,构造函数传入string赋予此常量, configAttribute.getAttribute()返回此常量*/ ConfigAttribute configAttribute = new SecurityConfig("ROLE_" + resources.getResKey()); configAttributes.add(configAttribute); resourceMap.put(resources.getResUrl(), configAttributes); } } } //返回所请求资源所需要的权限 public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAttributes(Object object) throws IllegalArgumentException { //从过滤链中获取当前请求 String requestUrl = ((FilterInvocation) object).getRequestUrl(); //如果资源角色库为空的话说明还未初始化 if(resourceMap == null) { loadResourceDefine(); //强制初始化 } //System.err.println("resourceMap.get(requestUrl); "+resourceMap.get(requestUrl)); //如果是get请求的话去掉后面参数 if(requestUrl.indexOf("?")>-1){ requestUrl=requestUrl.substring(0,requestUrl.indexOf("?")); } //获取该请求对应权限,url作为key Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes = resourceMap.get(requestUrl); return configAttributes; } }ExceptionTranslationFilter处理AuthenticationException和AccessDeniedException两种异常。
private void handleSpringSecurityException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, RuntimeException exception) throws IOException, ServletException { //如果异常是AuthenticationException(未登录即访问受保护资源) if (exception instanceof AuthenticationException) { //打印异常 this.logger.debug("Authentication exception occurred; redirecting to authentication entry point", exception); /*传入此方法后主要是调用AuthenticationEntryPoint的默认实现类 LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint中的commence方法重定向到登录页*/ this.sendStartAuthentication(request, response, chain, (AuthenticationException)exception); /* sendStartAuthentication源码 protected void sendStartAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, AuthenticationException reason) throws ServletException, IOException { SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication((Authentication)null); this.requestCache.saveRequest(request, response); this.logger.debug("Calling Authentication entry point."); this.authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response, reason); } */ } //如果是AccessDeniedException else if (exception instanceof AccessDeniedException) { //且是匿名用户(未登录即访问受保护资源;一般是该异常,少为AuthenticationException) if (this.authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(SecurityContextHolder .getContext().getAuthentication())) { this.logger.debug("Access is denied (user is anonymous); redirecting to authentication entry point", exception); //重定向到登录页,且把AccessDeniedException包装成AuthenticationException this.sendStartAuthentication(request, response, chain, new InsufficientAuthenticationException("Full authentication is required to access this resource")); } //非匿名用户(已登录但权限不足) else { this.logger.debug("Access is denied (user is not anonymous); delegating to AccessDeniedHandler", exception); //重定向到403页面;AccessDeniedHandler默认实现类:AccessDeniedHandlerImpl this.accessDeniedHandler.handle(request, response ,(AccessDeniedException)exception); } } }参考文章
- SSM整合SpringSecurity实现权限管理实例 javaconfig配置方式:做到了完全不用web.xml等任何配置文件,连bean的装载都全靠java类和注解完成。
- spring官方手册(从第6点看起)
- 在springboot中整合spring security并自定义验证代码
- SpringMVC + security模块 框架整合详解
- SpringSecurity——基于Spring、SpringMVC和MyBatis自定义SpringSecurity权限认证规则
- 自定义过滤器中有关AccessDecisionManager决策管理器的部分
- 有关ExceptionTranslationFilter
代码实例
- thz-manager-web/config
